ChatGPT and similar artificial intelligence tools have become part of daily life for millions of people around the world. These programs help users write emails, complete assignments, and communicate more effectively. However, recent research shows these tools are doing more than just assisting with tasks – they are actually changing how humans speak and write.
Scientists have discovered that people who use ChatGPT regularly begin adopting the language patterns and word choices that the AI system prefers. This shift happens without users being aware of it, and the changes appear in both written work and spoken conversation.
Key Takeaways
- Researchers found that certain words increased in usage by up to 51% after ChatGPT’s release
- The word “delve” has become a clear marker of AI influence in academic speech
- Brain scans show ChatGPT users complete tasks faster but show reduced mental activity
- Over 800 million people worldwide now use ChatGPT weekly
- Experts worry about the loss of individual expression and cultural diversity
The Vocabulary Shift
The Max Planck Institute for Human Development conducted a study of nearly 280,000 YouTube videos from academic channels. Researchers tracked how often speakers used specific words before and after ChatGPT’s launch in November 2022.
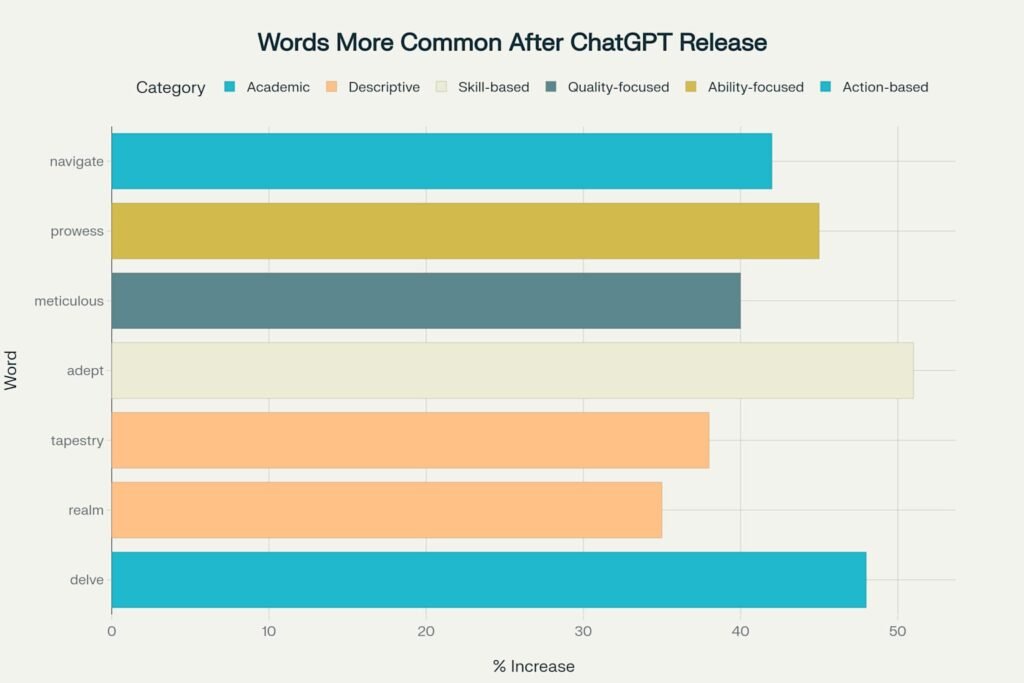
The results showed clear changes in word usage patterns. Terms like “delve,” “realm,” “adept,” and “tapestry” became much more common in spoken language. These are words that ChatGPT uses frequently in its responses.
Hiromu Yakura, who led the study, explained that people absorb this virtual vocabulary into their daily communication. The word “delve” stood out as particularly telling – it increased by 48% in usage and has become what researchers call a “linguistic watermark” that signals AI influence.
Effects on the Brain
Massachusetts Institute of Technology researchers studied how ChatGPT affects brain function by scanning 54 people aged 18-39 over four months. The participants were divided into three groups: those who used ChatGPT, those who used Google search, and those who worked without digital tools.
The brain scans revealed significant differences between groups. ChatGPT users completed tasks 60% faster than other participants. However, these same users showed 32% less mental effort during thinking tasks. The scans also showed weaker connections between brain regions in regular ChatGPT users.
Perhaps most concerning, 83% of ChatGPT users could not quote from essays they had written just minutes earlier. Teachers who reviewed the AI-assisted essays described them as lacking personal insight despite having correct grammar.
Scale of Adoption
The widespread use of these tools means their influence reaches far beyond individual users. Current adoption numbers show the massive scope of this change.
ChatGPT now has approximately 800 million weekly active users globally. In educational settings, 68% of college students use AI writing tools monthly. The business world has also embraced these technologies, with 92% of Fortune 100 companies using ChatGPT in some capacity.
The tool is available in 195 countries and supports over 95 languages. This global reach means the linguistic influence extends across different cultures and regions.
Expert Concerns About Communication
Researchers worry about the long-term effects on human expression. Mor Naaman, a professor at Cornell Tech who studies AI-mediated communication, has identified three areas of concern.
First, people lose authenticity in their communication when they rely on AI suggestions. Second, individuals put less effort into crafting their own messages. Third, people become less able to express their true thoughts and personality.
The concern extends beyond individual expression to cultural diversity. AI systems are typically trained on English-language data, which can lead to the dominance of Western communication styles. This process may reduce regional dialects and local language variations.
The Broader Cultural Impact
Language experts point out that communication diversity reflects cultural diversity. When everyone starts using similar words and phrases, it can flatten the rich variety that makes human interaction interesting.
The phenomenon creates what researchers call a “feedback loop”. As more people use AI-generated language, the training data for future AI systems becomes more uniform. This cycle could accelerate the loss of unique expression styles.
Some researchers worry this trend could affect creativity and original thinking. Language often sparks new ideas through unexpected word combinations. If AI systems push everyone toward the same predictable phrases, opportunities for creative breakthroughs may decrease.
Different Perspectives
Not all experts view these changes as entirely negative. Some argue that AI tools can help people communicate more clearly and efficiently. For individuals who struggle with writing or speaking in a second language, these tools provide valuable support.
Language professionals note that communication technology has always influenced how people express themselves. The printing press, telephone, and internet all changed language patterns in their time. Current AI influence may represent another step in this ongoing process.
However, most researchers emphasize the need for awareness about these changes. When people understand how AI affects their communication, they can make more conscious choices about when and how to use these tools.
Conclusion
The influence of ChatGPT and similar tools on human communication marks a major shift in how language develops. Research indicates these changes are occurring more quickly and extensively than past technological impacts on language.
The evidence points to both benefits and risks. Users gain speed and efficiency in their communication tasks. However, they may also lose some of their individual expression and cognitive engagement.
As these tools become more common, society faces important questions about preserving authentic human communication. The challenge lies in using AI assistance while maintaining the diversity and creativity that make human language rich and meaningful. Understanding these changes represents the first step toward making informed choices about the role of artificial intelligence in human expression.
References
- You sound like ChatGPT | The Verge
- Researchers Scanned the Brains of ChatGPT Users and Found Something Deeply Alarming
- ChatGPT Making People Dumb, Brains Of Youngsters At Highest Risk: Study
- AI Essay Writer Adoption in High School vs College: A Data Breakdown
- Number Of ChatGPT Users In 2025: Stats, Usage & Impact
- Losing Our Voice: The Human Cost of AI-Driven Language
- Linguistic Diversity in AI and Threats to Global Inclusion
- The Long-Term Impact of AI Language Prediction: Homogenization of Thought
- Humans Are Starting to Sound Like ChatGPT – Inbenta
- ChatGPT and the Homogenization of Language: How the Adoption of AI Silences Student Voices | ASCCC
- AI and the great linguistic flattening | UNESCO
- 500 ChatGPT Overused Words: Here’s How To Avoid Them – Workflows





